基本概念 前言 web开发:
web,网页的意思
静态web
html、css、js、mp4视频、jpg图片
界面数据不会发生变化
动态web
几乎所有的网站
提供给所有人看的数据始终发生变化,每个人在不同的时间,不同的地点获取的信息不同
技术栈:jsp页面、servlet程序
在Java中,动态web资源开发的技术统称为Javaweb
web应用程序 web应用程序:可以提供浏览器访问的程序
a.html,b.html….多个web资源,这些web资源可以被外界访问,对外界提供服务
这个统一的web资源会被放在同一个文件夹下,web应用程序—–>tomcat:服务器
一个web应用由多部分组成(静态web,动态web)
html,css,js
jsp,servlet
Java程序
jar包
配置文件(properties)
web应用程序编写完毕后,若想提供给外界访问:需要一个服务器来统一管理
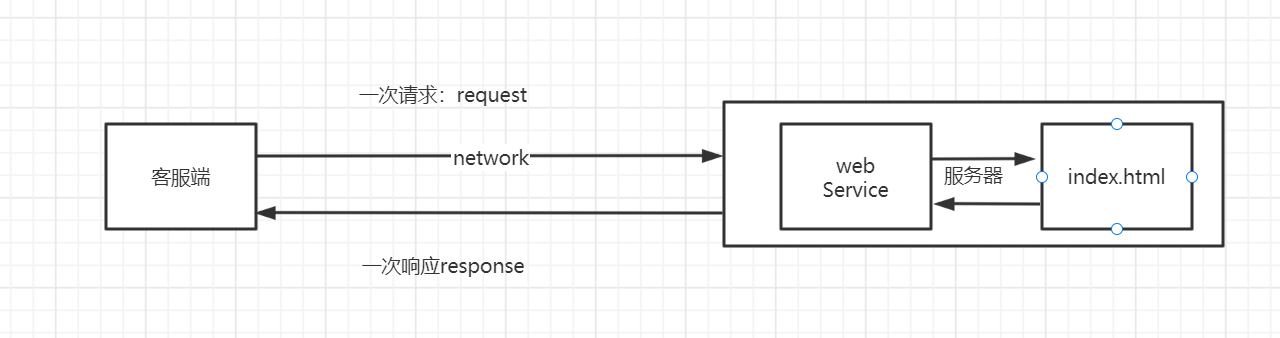
静态web
*.html,是网页的后缀,如果服务器上存在这个东西,我们就可以直接进行读取
静态web存在的缺点
web页面无法动态更新,所有用户看到都是同一个页面
无法和数据库交互(数据无法持久化,用户无法交互)
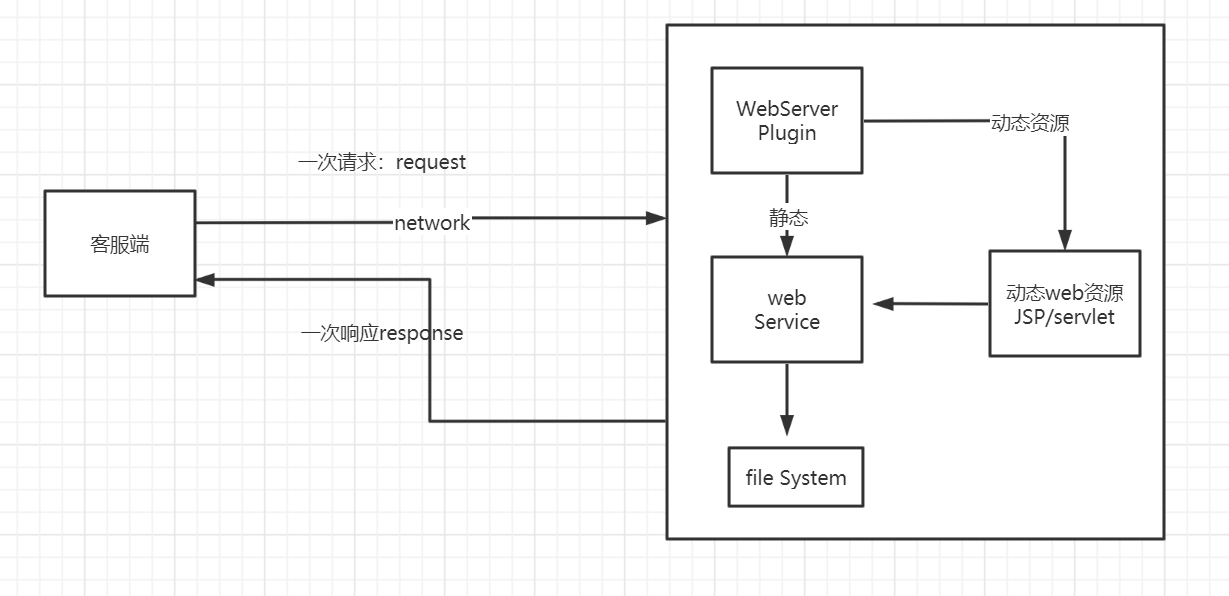
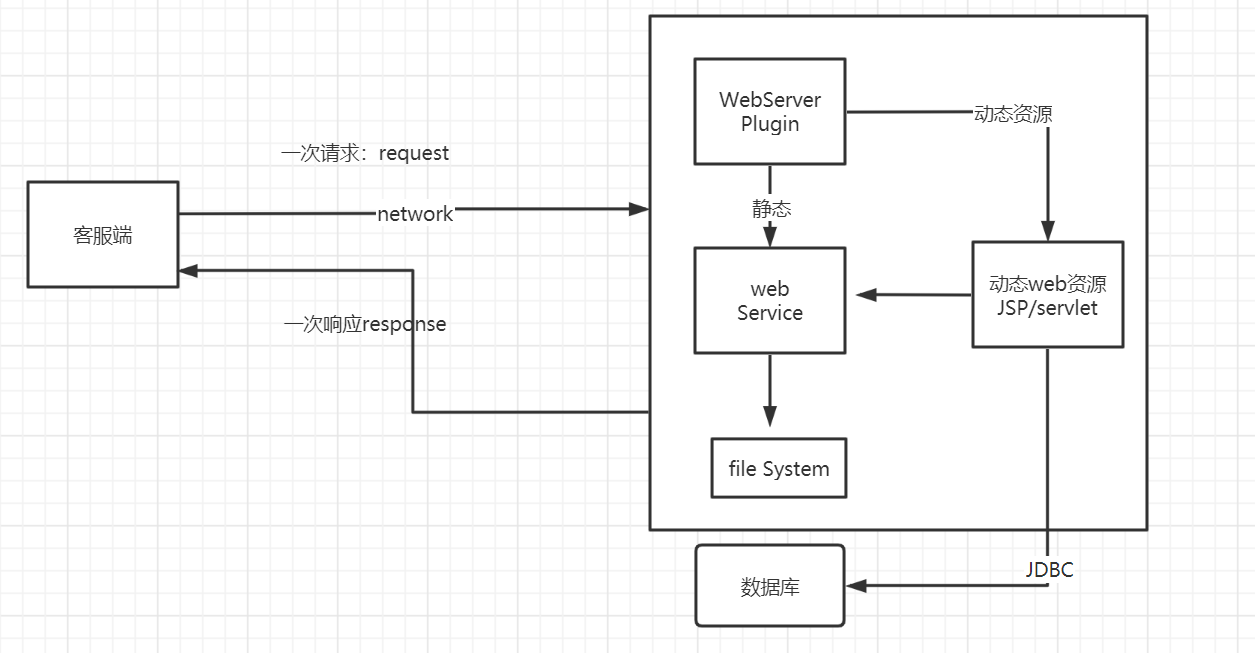
动态web 页面会动态展示
缺点:
加入服务器的动态web资源出现了错误,我们需要重新编写我们的后台程序,重新发布
优点:
web可以动态更新,所有用户看到都不是同一个页面
它可以与数据库交互
web服务器 技术 ASP
微软:国内最早流行的就是ASP
在HTML中嵌套了VB的脚本
在ASP开发中,基本一个页面都有几千行的业务代码,页面很乱
维护成本高
PHP
开发web方便便捷,适合中小型企业开发
不适合大型企业开发
JSP/Servlet:
B/S:浏览和服务器
C/S:客户端和服务器
sun公司主推的B/S架构
基于Java语言的(所有大公司,或者开源组件都是Java写的)
可以承载三高(高并发,高可用,高性能)问题带来的影响
服务器 tomcat
Tomcat是Apache 软件基金会(Apache Software Foundation)的Jakarta 项目中的一个核心项目,由Apache 、Sun 和其他一些公司及个人共同开发而成。由于有了Sun 的参与和支持,最新的Servlet 和JSP 规范总是能在Tomcat 中得到体现,因为Tomcat 技术先进、性能稳定,而且免费 ,因而深受Java 爱好者的喜爱并得到了部分软件开发商的认可,成为目前比较流行的Web 应用服务器。
Tomcat 服务器是一个免费的开放源代码的Web 应用服务器,属于轻量级应用服务器 ,在中小型系统和并发访问用户不是很多的场合下被普遍使用,是开发和调试JSP 程序的首选。对于一个初学者来说是最佳选择
Tomcat 实际上运行JSP 页面和Servlet
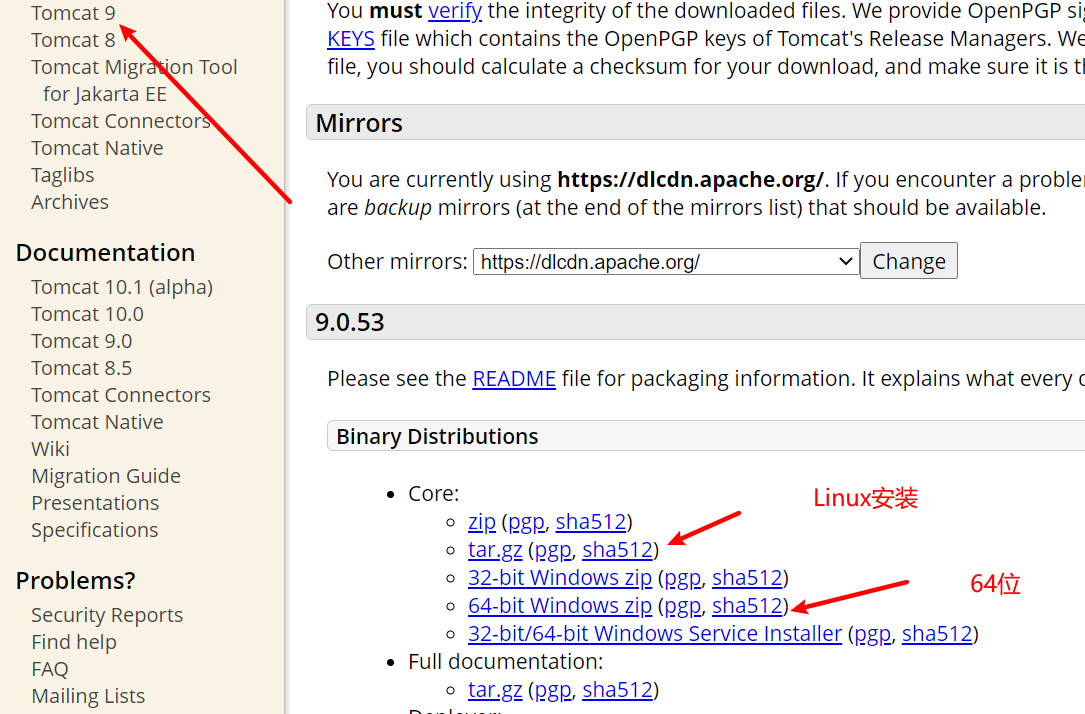
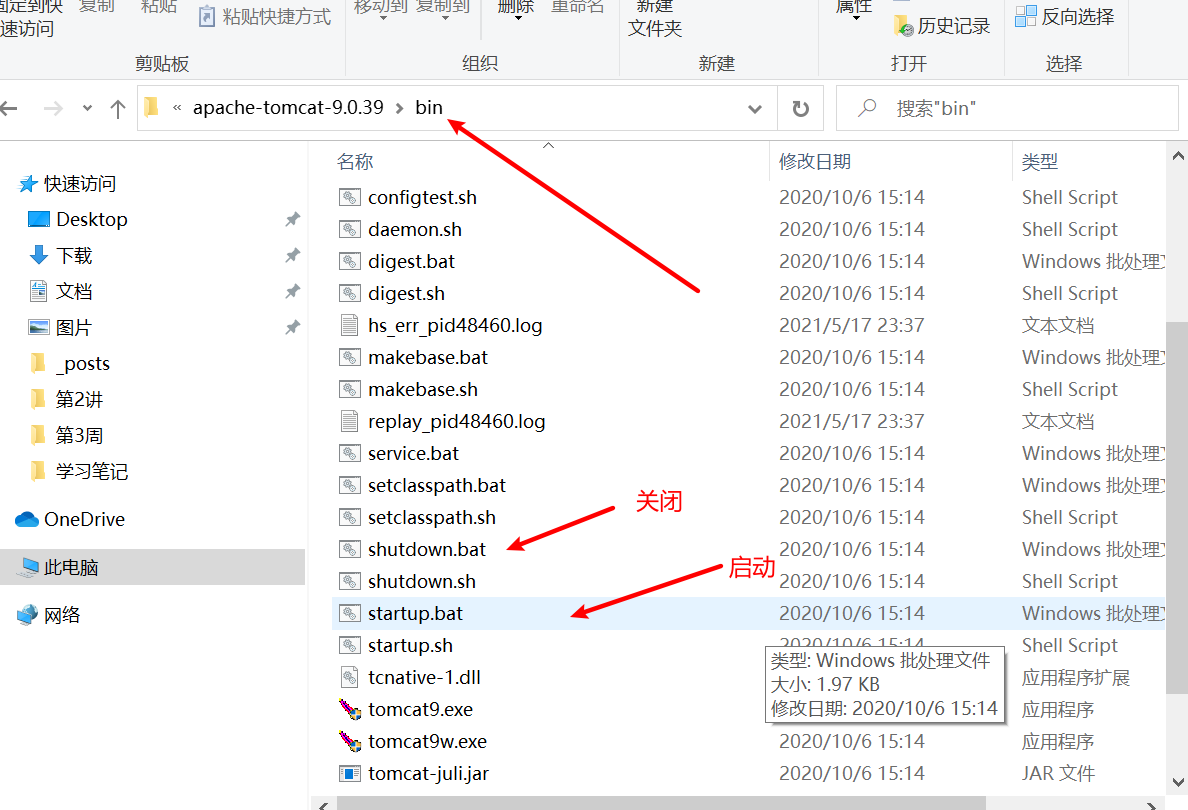
tomcat的使用 tomcat安装 tomcat官网: https://tomcat.apache.org/
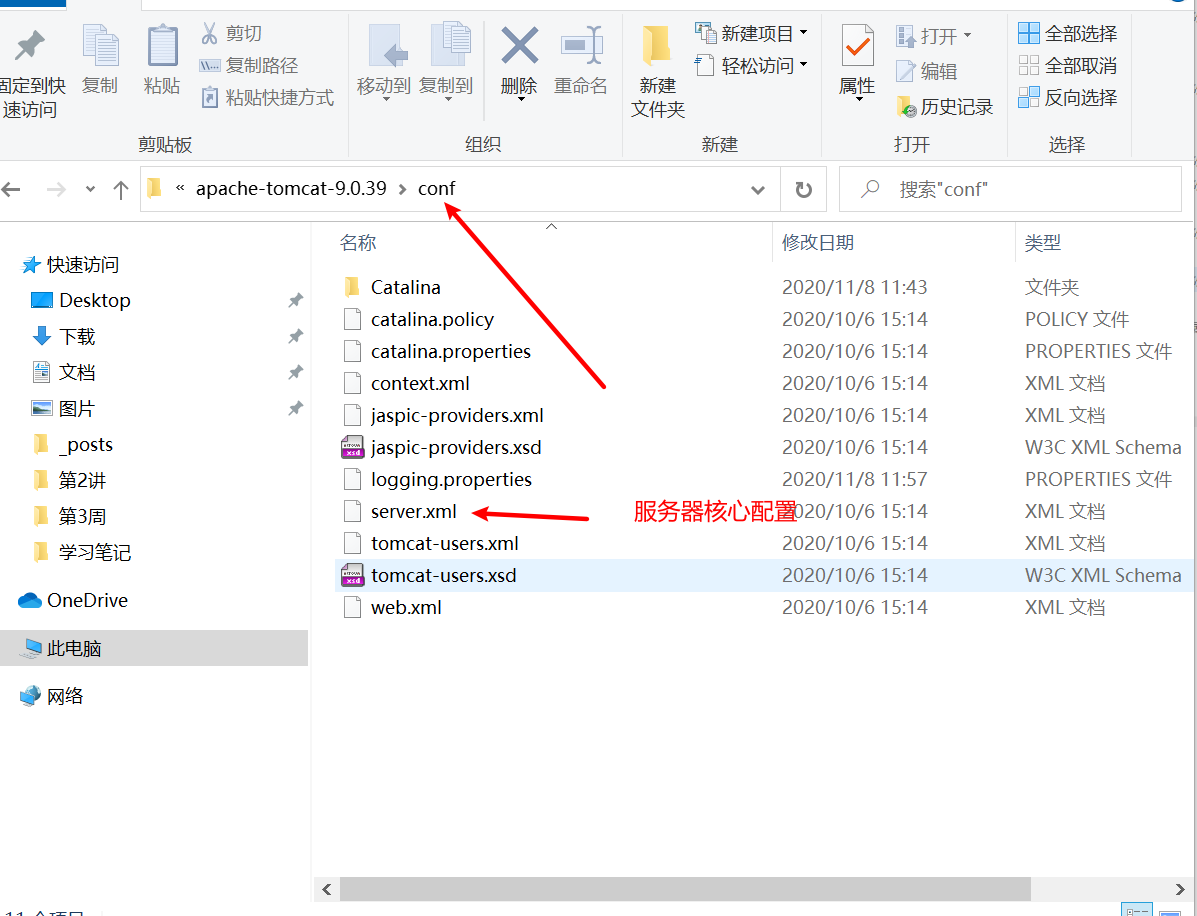
tomcat目录介绍
bin 专门用来存放tomcat服务器的可执行程序
conf 专门用来存放tomcat服务器的配置文件
lib 专门用来存放tomcat服务区的jar包
logs 专门用来存放tomcat服务器运行时输出的日记信息
temp 专门用来存放tomcat运行时产生的临时数据
webapp 专门存放部署的web工程
work 是tomcat工作时的目录,用来存放tomcat运行时jsp翻译为servlet的源码,和session钝化的目录
tomcat的启动方式 可能遇到的问题:
Java环境变量没有配置
闪退问题:需要配置兼容性
乱码问题:配置文件中设置
配置 可以配置端口号:
tomcat的默认端口号为:8080
MySQL:3306
http:80
https:443
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1" "20000" "8443" />
可以配置主机的名称:
默认的主机名为:localhost—>127.0.0.1
默认网站应用存放位置:webapps
<Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps" "true" autoDeploy="true" >
面试题:
谈谈网站是如何进行访问的:
输入一个域名:回车
检查本机的C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts配置文件下有没有这个域名映射
有:直接返回对应的IP地址,这个地址中,有我们需要访问的web程序,可以直接访问
没有:去DNS服务器找,找到的话就返回,找不到就返回找不到
发布一个web网站 将写好的网站,放到服务器(tomcat)中指定的web应用的文件夹(webapps)下,就可以访问了
网站应有的结构
--webapps:tomcat服务器的web目录
Http
HTTP(超文本传输协议)是一个简单的请求-响应协议,它通常运行在TCP之上
文本:HTML,字符串
超文本:图片,音乐,定位,地图
默认端口号:80
Https:安全的
两个时代
http1.0
HTTP/1.0:客户端可以与web服务器连接后,只能获得一个web资源,断开连接
http2.0
HTTP/1.1:客户端可以与web服务器连接后,可以获得多个web资源
Http请求
百度
Request URL: https:200 OK 状态码:200 14.215 .177 .38 :443 远程地址
请求行
请求行中请求方式:GET
请求方式:Get,Post,Head,Delete,Put,Tract……
get:请求能够携带的参数比较少,大小有限制,会在浏览器的URL地址栏显示数据内容,不安全,但高效
post:请求能够携带的参数没有限制,大小没有限制,会在浏览器的URL地址栏显示数据内容,安全,但不高效
消息头 Accept: 告诉浏览器,它所支持的数据类型8 GB2312 ISO8859-1 0.9 告诉浏览器,它的语言环境0 缓存控制
Http响应
百度:
Cache-Control: private 缓存控制8 类型
响应体 Accept: 告诉浏览器,它所支持的数据类型8 GB2312 ISO8859-1
响应状态码 200:请求响应成功 200
3xx:请求重定向
重定向:重新定位到另一个地址
4xx:找不到资源 404
资源不存在
5xx:服务器代码错误 502:网关错误
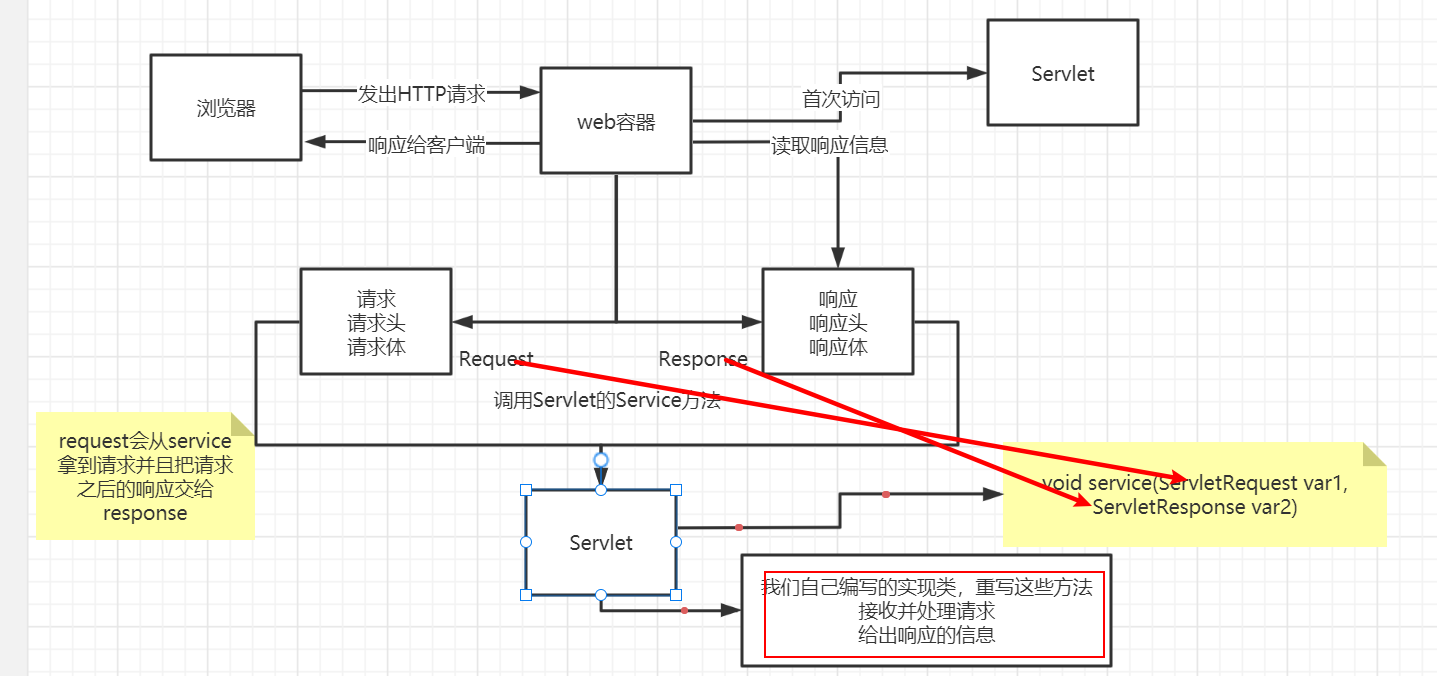
Servlet Servlet简介
servlet是sun公司开发动态web的一门技术
sun在这些API中提供了一个接口叫做:Servlet, 编写一个servlet程序,只需要完成两个小步骤
编写一个类,实现servlet接口
把开发好的Java类部署到web服务器中
把实现了servlet接口的Java程序叫做,Servlet
HelloServlet
编写一个普通类
实现servlet接口,这里我们直接继承HttpServlet
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet @Override protected void doGet (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException "进入了doGet方法" );"hello world" );@Override protected void doPost (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
编写servlet的映射
为什么需要映射:我们写的是Java程序,但是需要通过浏览器访问,而浏览器需要连接web服务器,所以我们需要再web服务中注册我们写的servlet,还需给一个浏览器能够访问的路径
<servlet > <servlet-name > hello</servlet-name > <servlet-class > com.sise.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > hello</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /hello</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping >
启动tomcat服务器
访问请求地址
Servlet原理
Mapping问题
一个servlet可以指定一个映射路径
一个servlet可以指定多个映射路径
一个servlet可以指定通用映射路径
<servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > hello</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /*</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping >
指定一些后缀等等
//可以自定义后缀实现请求映射<servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > hello</servlet-name > <url-pattern > *.zhangsan</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping >
优先级问题
指定了固有的映射路径优先级最高,如果找不到就会走默认的处理请求
ServletContext web容器在启动的时候,它会为每个web程序都创建一个对应的ServletContext对象,它代表了当前的web应用
共享数据 在这个servlet中保存数据,可以在另外一个servlet中拿到
public class SetContext extends HttpServlet @Override protected void doGet (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException this .getServletContext();"张三" ;"name" ,name);@Override protected void doPost (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class GetContext extends HttpServlet @Override protected void doGet (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException "text/html" );"utf-8" );this .getServletContext();"name" );"姓名:" +name);@Override protected void doPost (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
<servlet > <servlet-name > set</servlet-name > <servlet-class > com.sise.context.SetContext</servlet-class > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > set</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /set</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping > <servlet > <servlet-name > get</servlet-name > <servlet-class > com.sise.context.GetContext</servlet-class > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > get</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /get</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping >
获取初始化参数
web.xml配置初始化参数
<context-param > <param-name > url</param-name > <param-value > jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306</param-value > </context-param >
编写class
public class GetParameter extends HttpServlet @Override protected void doGet (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException this .getServletContext();"url" );@Override protected void doPost (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
编写映射文件
<servlet > <servlet-name > parameter</servlet-name > <servlet-class > com.sise.context.GetParameter</servlet-class > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > parameter</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /parameter</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping >
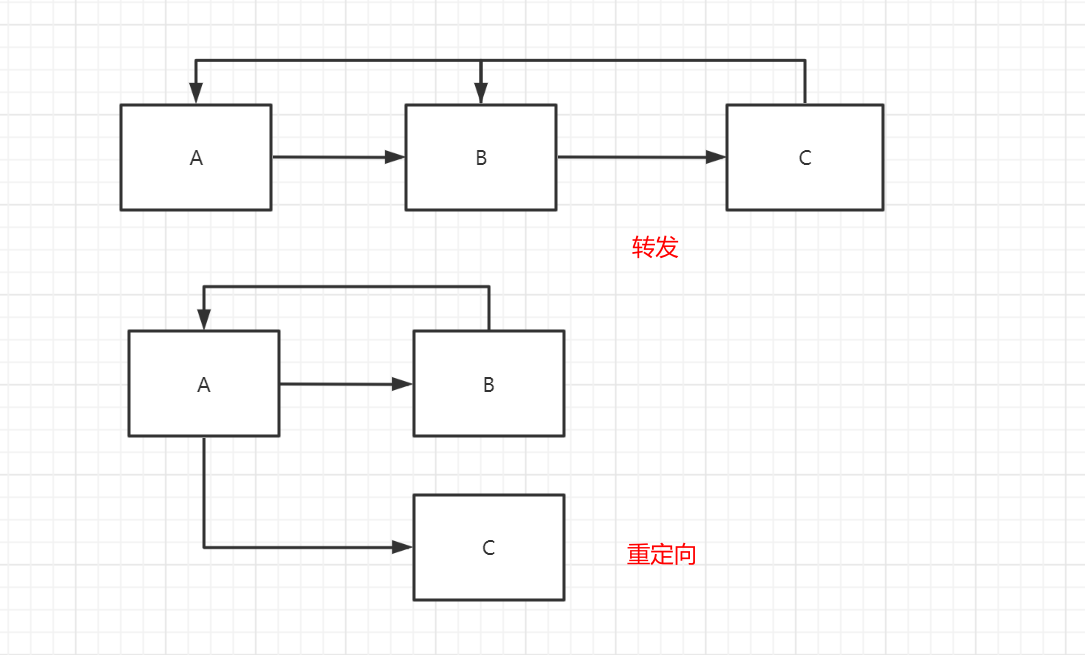
请求转发
编写类
public class Forward extends HttpServlet @Override protected void doGet (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException this .getServletContext();"/parameter" ).forward(req,resp);@Override protected void doPost (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
web.xml
<servlet > <servlet-name > forward</servlet-name > <servlet-class > com.sise.context.Forward</servlet-class > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > forward</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /forward</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping >
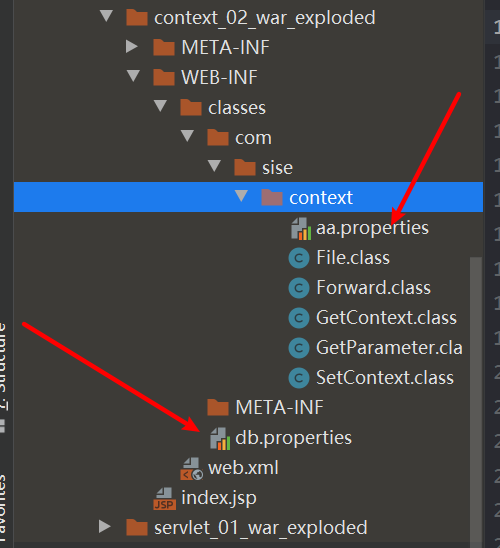
读取资源文件 properties
在Java目录下新建properties,会识别不了,需要增加maven资源过滤
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 <build > <resources > <resource > <directory > src/main/resources</directory > <includes > <include > **/*.properties</include > <include > **/*.xml</include > </includes > </resource > <resource > <directory > src/main/java</directory > <includes > <include > **/*.properties</include > <include > **/*.xml</include > </includes > </resource > </resources > </build >
发现都被打包到了同一个路径下:classes,我们俗称这个路径为classpath
public class File extends HttpServlet @Override protected void doGet (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException this .getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/WEB-INF/classes/com/sise/context/aa.properties" );new Properties();"username" );"password" );"===" +password);@Override protected void doPost (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
<servlet > <servlet-name > file</servlet-name > <servlet-class > com.sise.context.File</servlet-class > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > file</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /file</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping >
HttpServletResponse web服务器接收到客户端的http请求,针对这个请求,分别创建一个代表请求的HttpServletRequest对象,代表响应的一个HttpServletResponse
如果要获取客户端请求过来的参数:找HttpServletRequest
如果要给客户端响应一些信息:HttpServletResponse
简单分类 负责向浏览器发送数据的方法
ServletOutputStream getOutputStream () throws IOException ;PrintWriter getWriter () throws IOException ;
负责向浏览器发送响应头的方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 void setCharacterEncoding (String var1) void setContentLength (int var1) void setContentLengthLong (long var1) void setContentType (String var1) void setDateHeader (String var1, long var2) void addDateHeader (String var1, long var2) void setHeader (String var1, String var2) void addHeader (String var1, String var2) void setIntHeader (String var1, int var2) void addIntHeader (String var1, int var2)
响应状态码
int SC_CONTINUE = 100 ;int SC_SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS = 101 ;int SC_OK = 200 ;int SC_CREATED = 201 ;int SC_ACCEPTED = 202 ;int SC_NON_AUTHORITATIVE_INFORMATION = 203 ;int SC_NO_CONTENT = 204 ;int SC_RESET_CONTENT = 205 ;int SC_PARTIAL_CONTENT = 206 ;int SC_MULTIPLE_CHOICES = 300 ;int SC_MOVED_PERMANENTLY = 301 ;int SC_MOVED_TEMPORARILY = 302 ;
常用应用 下载文件
要获取下载文件的路径
下载的文件名是啥?
设置想办法让浏览器能够支持下载我们需要的东西
获取下载文件的输入流
创建缓冲取
获取OutputStream对象
将FileOutputStream流写入到buffer缓冲区
使用OutputStream将缓冲区中的数据输出到客户端
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public class FileServlet extends HttpServlet @Override protected void doGet (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException "D:\\IdeaProject\\JavaWeb\\response-03\\target\\classes\\1.jpg" ;"下载文件的路径" +realPath);"\\" ) + 1 );"Content-Disposition" ,"attachment;filename=" +fileName);new FileInputStream(realPath);int len = 0 ;byte [] buffer = new byte [1024 ];while ((len=fileInputStream.read(buffer))>0 ){0 ,len);@Override protected void doPost (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
画图片 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 public class ImageServlet extends HttpServlet @Override protected void doGet (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException "refresh" ,"3" );new BufferedImage(80 , 20 , BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);0 ,0 ,80 ,20 );new Font(null ,Font.BOLD,20 ));0 ,20 );"image/jpeg" );"expires" ,-1 );"Cache-Control" ,"no-cache" );"pragma" ,"no-cache" );"jpg" ,resp.getOutputStream());private String makeNum () new Random();9999999 ) + "" ;new StringBuffer();for (int i = 0 ; i < 7 - num.length(); i++) {"0" );return num;@Override protected void doPost (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
重定向 B一个web资源收到客户端A请求后,它会通知A客户端去访问另外一个web资源C,这个过程叫做重定向
常用场景:
public class RequestServlet extends HttpServlet @Override protected void doGet (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException "/imageServlet" );@Override protected void doPost (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
用户登录重定向案例:
类:
public class RequestTest extends HttpServlet @Override protected void doGet (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException "进入了JSP界面" );"username" );"password" );"==" +password);"/success.jsp" );@Override protected void doPost (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
index.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>"${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login" method="get" >"text" name="username" ><br>"password" name="password" ><br>"submit" >
success.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
映射路径
<servlet > <servlet-name > requestTest</servlet-name > <servlet-class > com.sise.response.RequestTest</servlet-class > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > requestTest</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /login</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping >
HttpServletRequest HttpServletRequest代表客户端的请求,用户通过http协议访问服务器,HTTP请求中的所有信息会被封装到HttpServletRequest,通过这个HttpServletRequest的方法,获得客户端的所有信息
获取参数,请求转发 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class RequestServlet extends HttpServlet @Override protected void doGet (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException @Override protected void doPost (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException "utf-8" );"username" );"password" );"hobbies" );"utf-8" );"/success.jsp" ).forward(req,resp);
index.jsp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>"${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login" method="post" >"text" name="username" ><br>"password" name="password" ><br>"checkbox" name="hobbies" value="女孩" >女孩"checkbox" name="hobbies" value="代码" >代码"checkbox" name="hobbies" value="电影" >电影"checkbox" name="hobbies" value="英语" >英语"submit" >
success.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
请求映射
<servlet>class >com .sise .servlet .RequestServlet </servlet -class ></servlet > <servlet -mapping > <servlet -name >requestServlet </servlet -name > <url -pattern >/login </url -pattern > </servlet -mapping >
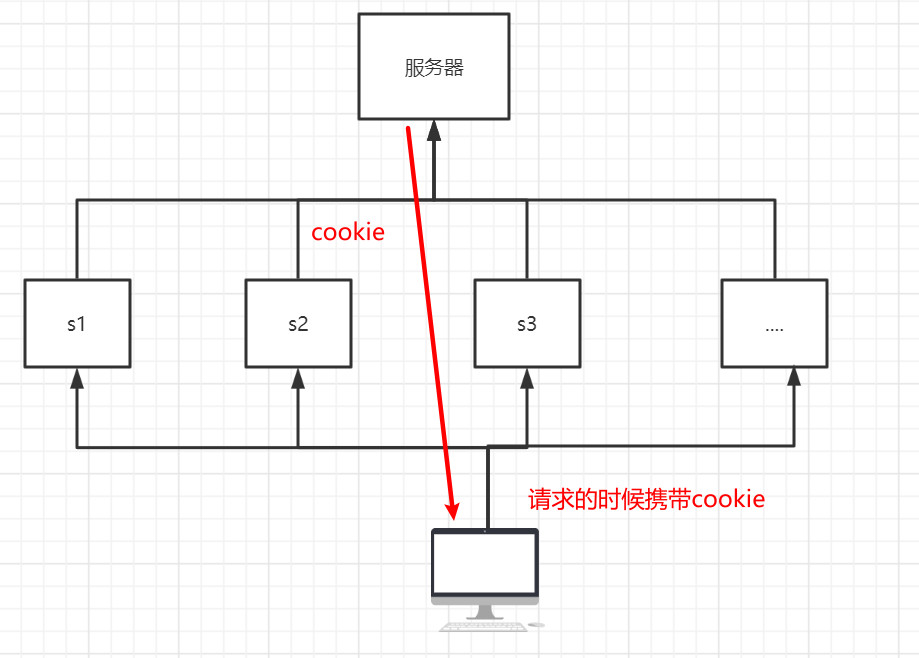
Cookie、Session 会话 会话 :用户打开一个浏览器,点击了很多超链接,访问多个web资源,关闭浏览器,这个过程可以称之为会话
有状态会话 :一个同学来过教室,下次再来教室,我们会知道这个同学曾经来过
一个网站,怎么证明你来过?
客户端 服务端
服务端给客户端一个信件,客户端下次访问服务端带上信件就可以了;cookie
服务器登录你来过了,下次你来的时候我来匹配你;session
保存会话的两种技术 cookie:
客户端技术(响应,请求)
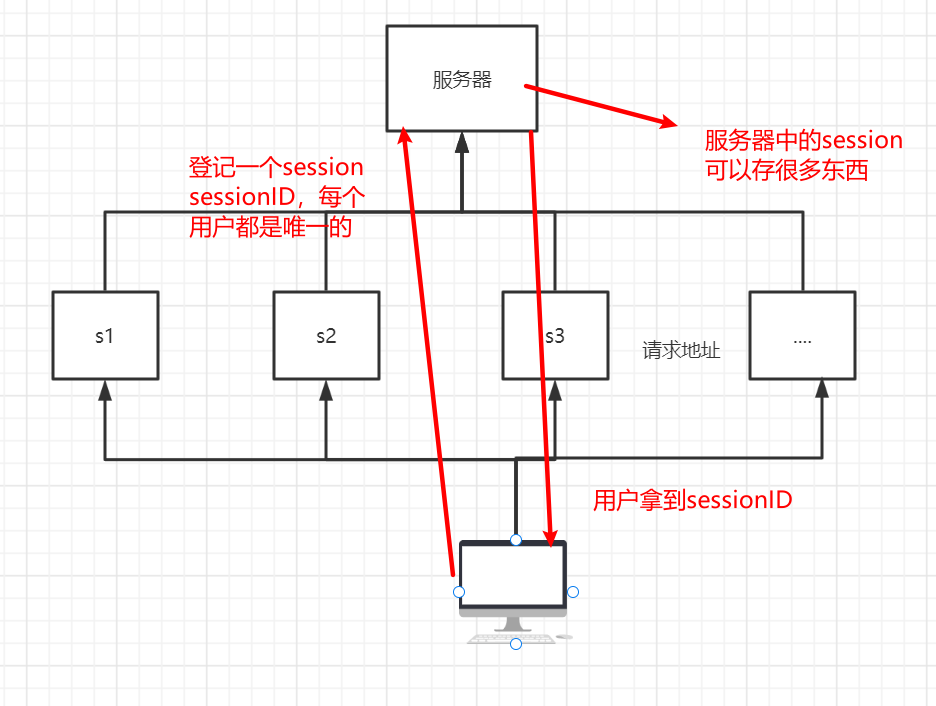
session:
服务器技术,利用这个技术,可以保存用户的会话信息?我们可以把信息或者数据放在session中
常见:网站登录之后,你下次不用再登录,第二次访问直接上去了
cookie
从请求中拿到cookie信息
服务器响应给客户端cookie
Cookie[] cookies = req.getCookies(); new Cookie("lastLoginTime" , System.currentTimeMillis() + "" ); 24 *60 *60 );
一个网站cookie是否存在上限
一个cookie只能保存一个信息
一个web站点可以给浏览器发送多个cookie,最多存放20个cookie
cookie大小有限制4KB
300个cookie浏览器上限
删除cookie:
不设置有效期,关闭浏览器,自动失效
设置有效期时间为0
session 什么是session:
服务器会给每一个用户(浏览器)创建一个session对象
一个session独占一个浏览器,只要浏览器没有关闭,这个session就存在
用户登录之后,整个网站都可以访问了—>保存用户的信息,保存购物车的信息
session和cookie的区别:
cookie是把用户的数据写给用户的浏览器,浏览器保存(可以保存多个)
session把用户的数据写给到用户独占的session中,服务器端保存(保存重要的信息,减少服务器资源的浪费)
session对象由服务创建
使用场景:
保存一个登录用户的信息
购物车信息
在整个网站中经常会使用的数据
JSP 什么是JSP Java server pags:Java服务器端页面,也和servlet一样,用于动态web技术
最大的特点:
写jsp就像在写HTML
区别:
HTML只给用户提供静态的数据
jsp页面中可以嵌入Java代码,为用户提供动态数据
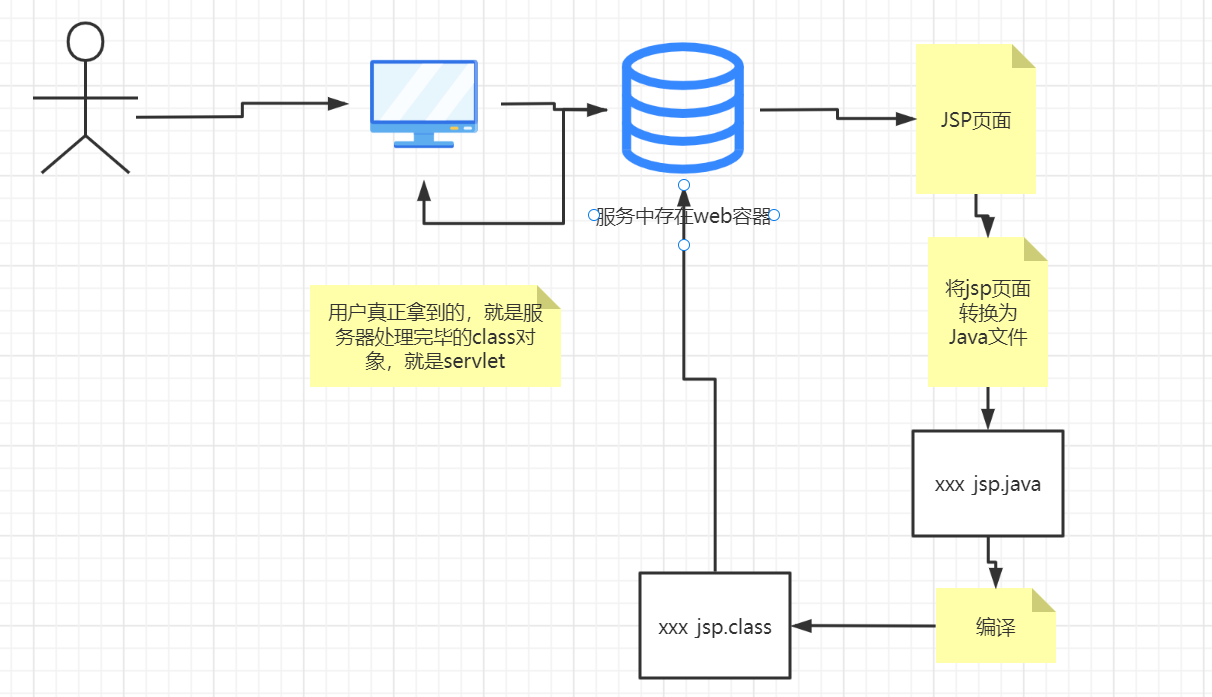
JSP原理 思路:jsp到底怎么执行的
浏览器向服务器发送请求,不管访问什么资源,其实都在访问servlet
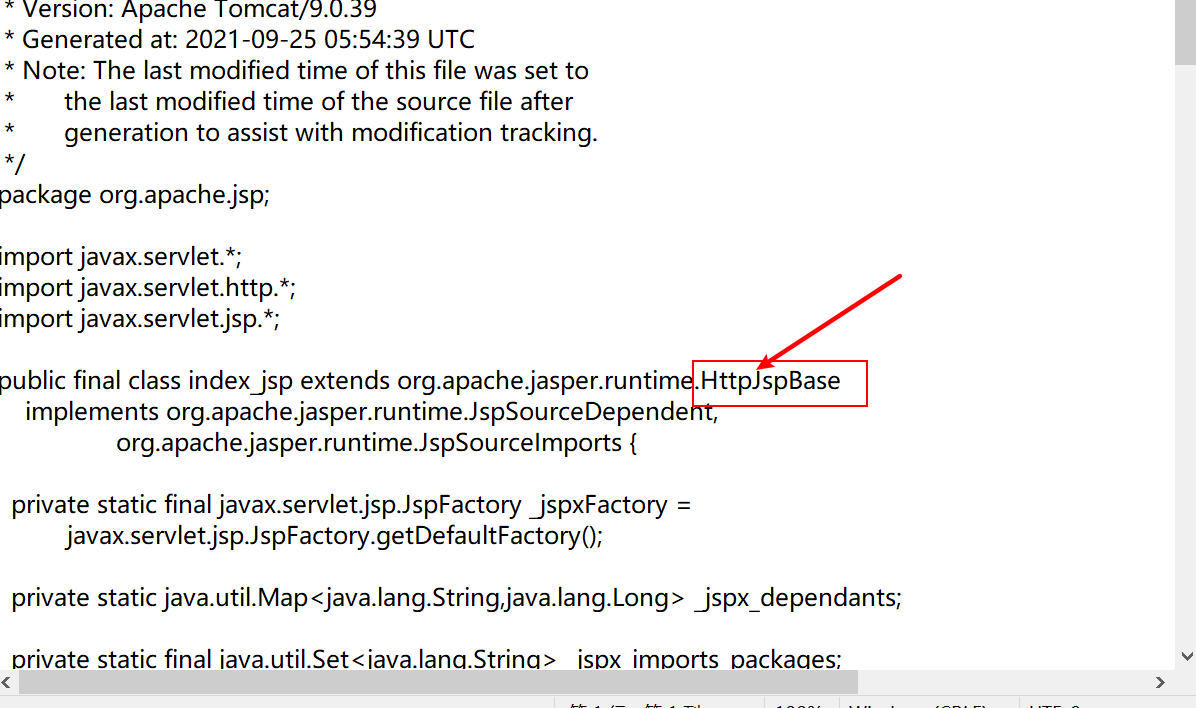
JSP最终也会被转换成为一个Java类
JSP本质就是一个servlet
源码分析:
public void _jspInit () public void _jspDestroy () public void _jspService (final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request, final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response) throws java.io.IOException, javax.servlet.ServletException {}
判断请求
public void _jspService (final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request, final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response) throws java.io.IOException, javax.servlet.ServletException {if (!javax.servlet.DispatcherType.ERROR.equals(request.getDispatcherType())) {final java.lang.String _jspx_method = request.getMethod();if ("OPTIONS" .equals(_jspx_method)) {"Allow" ,"GET, HEAD, POST, OPTIONS" );return ;if (!"GET" .equals(_jspx_method) && !"POST" .equals(_jspx_method) && !"HEAD" .equals(_jspx_method)) {"Allow" ,"GET, HEAD, POST, OPTIONS" );"JSP 只允许 GET、POST 或 HEAD。Jasper 还允许 OPTIONS" );return ;
内置一些对象
final javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext pageContext; null ; final javax.servlet.ServletContext application; final javax.servlet.ServletConfig config; null ; final java.lang.Object page = this ;
输出页面前增加的代码
try {"text/html;charset=UTF-8" ); this , request, response,null , true , 8192 , true );
以上这个对象我们都可以在JSP页面中直接使用
在JSP页面中:
只要是Java代码就会原封不动的输出
如果是HTML代码就会转换为
这样格式,输出到前端
JSP基础语法 JSP作为Java技术的一种应用,Java的所有语法都支持,它还会自己扩充一些语法(了解即可)
jsp表达式 <%--new java.util.Date()%>
jsp脚本片段 <%int sum = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < 100 ; i++) {
jsp脚本插入HTML元素 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <%int x = 5 ;5 );int y = 10 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) {
jsp声明 <%!static {"Loading Servlet" );private int globalVar = 0 ;public void test () "进入test方法" );
jsp声明:会被编译到jsp生成Java的类中,其他的,都会被生成_jspService方法中
在jsp中,嵌入Java代码即可
jsp的注释,不会在客户端显示,HTML就会
jsp指令
定制页面错误<%@ page errorPage=”error/500.jsp” %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>"error/500.jsp" %>int x = 1 /0 ;
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>"../image/1.png" >
也可以在web.xml中定义
<error-page>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>"error/500.jsp" %>--%>int x = 1 /0 ;
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>"../image/1.png" >
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>@include file="common/header.jsp" %><hr/>@include file="common/footer.jsp" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
9大内置对象
PageContext 存东西
Request 存东西
Response
Session 存东西
Application [ServletContext]存东西
config 【ServletConfig】
out
page
exception
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>"name1" ,"张三1号" );"name2" ,"张三2号" );"name3" ,"张三3号" );"name4" ,"张三4号" );"name1" );"name2" );"name3" );"name4" );"name5" );
request:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,用户看完就没用了,比如:新闻,用户看完就没用了
session:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,用户用完一会还有用,比如:购物车
application:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,一个用户用完了,其他用户还可能使用,比如:聊天数据
JSP标签、JSTL标签、EL表达式 <dependency > <groupId > javax.servlet.jsp.jstl</groupId > <artifactId > jstl-api</artifactId > <version > 1.2</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > taglibs</groupId > <artifactId > standard</artifactId > <version > 1.1.2</version > </dependency >
jsp标签 <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>1 "jsptag2.jsp" >"name" value="张三" />"age" value="20" />
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>2 "name" )%>"age" )%>
页面乱码问题为解决
JSTL标签 JSTL标签库的使用就是为了弥补HTML标签的不足,它自定义许多标签,可以供我们使用,标签的功能和Java代码一样
使用步骤:
引入对应的标签库
使用其中的方法
标签库解析错误:在tomcat也需要引入jstl的包,否则就会报jstl解析错误
c:if
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>"c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>"jstltag.jsp" method="get" >"text" name="username" value="${param.username}" >"submit" value="登录" >if test="${param.username=='admin'}" var ="isAdmin" >"登录成功" />"${isAdmin}" />
c:foreach
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 <%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>import ="java.util.ArrayList" %>import ="java.util.List" %>"text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>new ArrayList<>();0 ,"张三" );1 ,"李四" );2 ,"王五" );3 ,"赵六" );4 ,"田七" );"list" ,people);var :每一次遍历的变量var ="people" items="${list}" >"${people}" /><br>var ="people" items="${list}" begin="1" end="3" step="1" >"${people}" /><br>
El表达式
JavaBean 实体类
JavaBean有特定的写法:
必须要有一个无参构造
属性私有化
必须有对应的get/set方法
一般用来和数据库的字段做映射 ORM
实体类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 package com.sise.pojo;public class Person private String name;private int id;private int age;private String address;public Person () public Person (String name, int id, int age, String address) this .name = name;this .id = id;this .age = age;this .address = address;public String getName () return name;public void setName (String name) this .name = name;public int getId () return id;public void setId (int id) this .id = id;public int getAge () return age;public void setAge (int age) this .age = age;public String getAddress () return address;public void setAddress (String address) this .address = address;@Override public String toString () return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", id=" + id +", age=" + age +", address='" + address + '\'' +'}' ;
jsp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>"person" class "com.sise.pojo.Person" scope="page" />"person" property="name" value="张三" />"person" property="id" value="1" />"person" property="age" value="18" />"person" property="address" value="广东" />"person" property="name" />"person" property="id" />"person" property="age" />"person" property="address" />
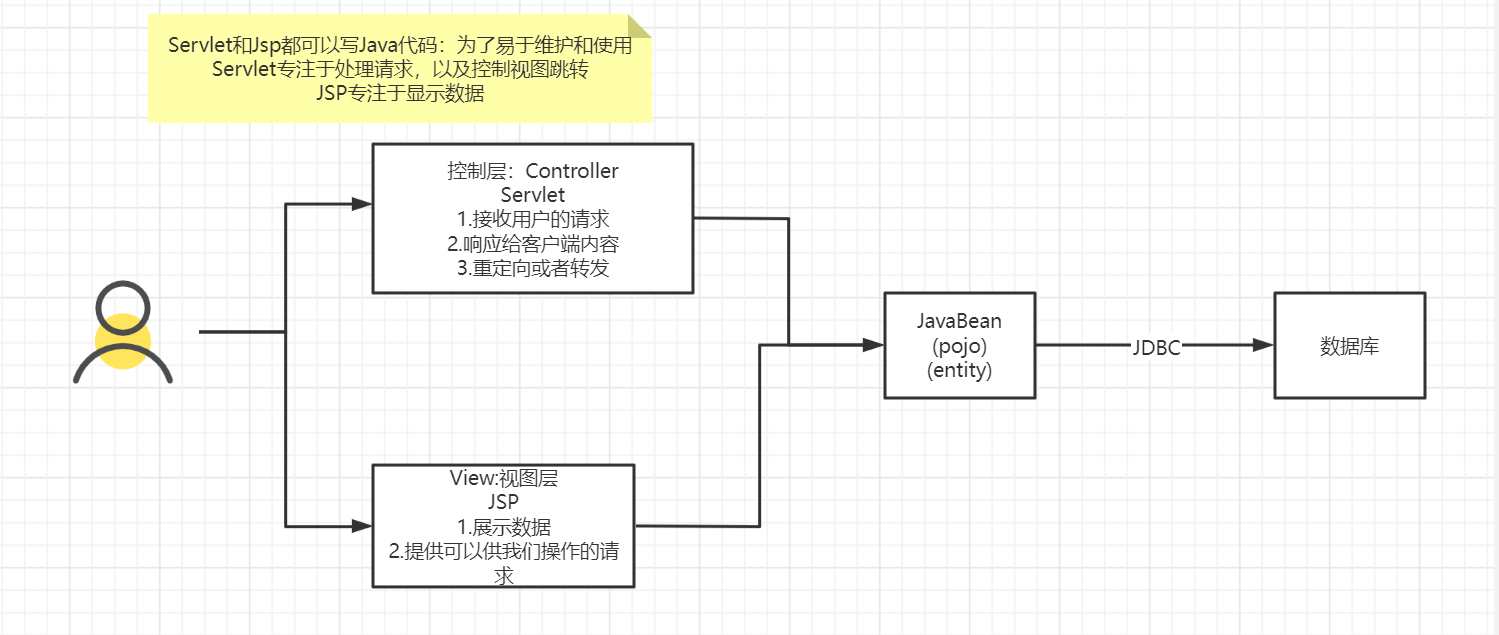
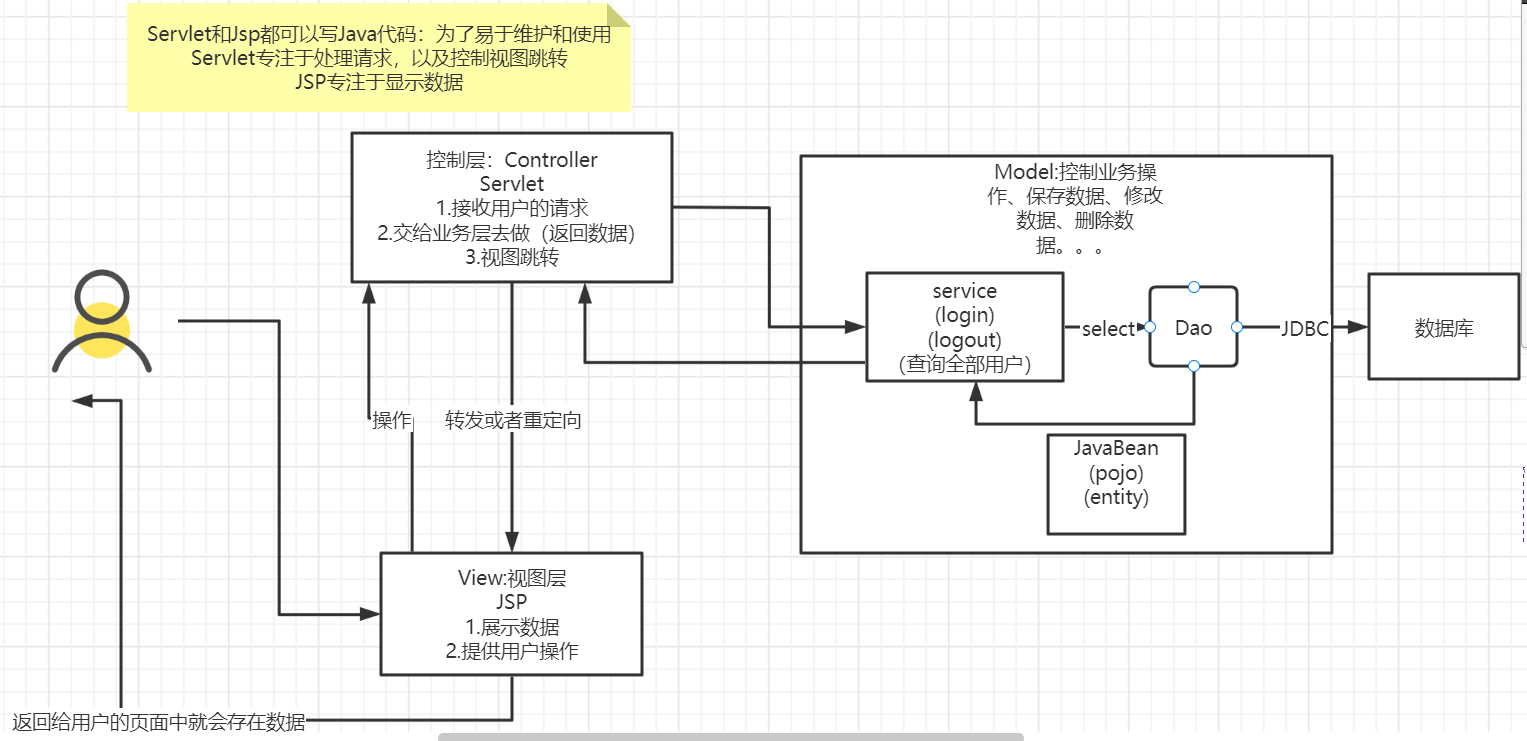
MVC三层架构 MVC:Model View Controller 模型、视图、控制器
早些年
用户直接访问控制层,控制层就可以直接操作数据库
servlet---CRUD---数据库
MVC三层架构
Model
业务处理:业务逻辑(Service)
数据持久层:CRUD (DAO)
View
展示数据
提供链接发起Servlet请求(a form img)
Controller(Servlet)
接收用户的请求:(req:请求参数、Session信息)
交给业务层处理对应的代码
控制视图的跳转
登录--->接收用户的登录请求---->处理用户的请求(获取用户登录的参数,username,password)--->交给业务层处理登录业务(判断用户名密码是否正确:事务)---->Dao层查询用户名和密码是否正确---->数据库
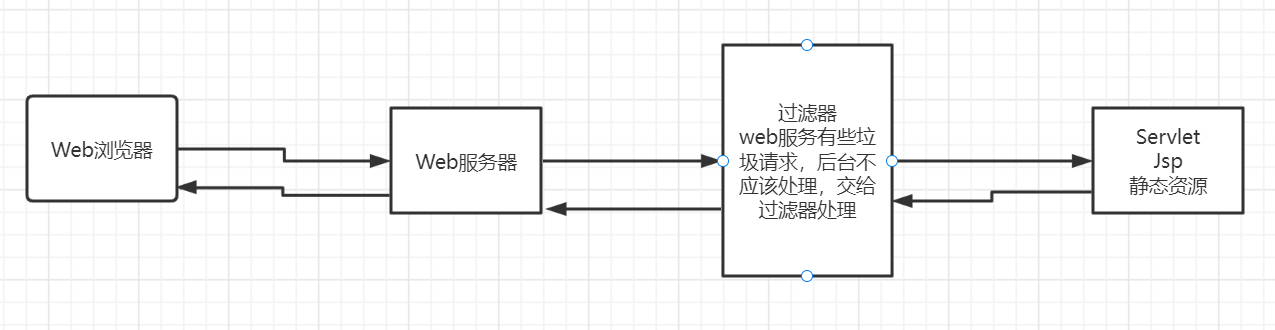
Filter Filter:过滤器,用来过滤网站的数据
实现filter接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class CharacterEncodingFilter implements Filter public void init (FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException "CharacterEncodingFilter初始化" );public void doFilter (ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException "utf-8" );"utf-8" );"text/html;charset=UTF-8" );"CharacterEncodingFilter执行前。。。" );"CharacterEncodingFilter执行后。。。" );public void destroy () "CharacterEncodingFilter销毁" );
编写测试类
public class ShowServlet extends HttpServlet @Override protected void doGet (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException "你好呀,世界" );@Override protected void doPost (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException
配置web.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 <servlet > <servlet-name > ShowServlet</servlet-name > <servlet-class > com.sise.servlet.ShowServlet</servlet-class > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > ShowServlet</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /show</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > ShowServlet</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /servlet/show</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping > <filter > <filter-name > CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name > <filter-class > com.sise.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class > </filter > <filter-mapping > <filter-name > CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name > <url-pattern > /servlet/*</url-pattern > </filter-mapping >
监听器 实现一个监听器接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public class SessionListener implements HttpSessionListener public void sessionCreated (HttpSessionEvent httpSessionEvent) "OnlineCount" );if (onlineCount==null ){new Integer(1 );else {int count = onlineCount.intValue();new Integer(count+1 );"OnlineCount" ,onlineCount);public void sessionDestroyed (HttpSessionEvent httpSessionEvent) "OnlineCount" );if (onlineCount==null ){new Integer(0 );else {int count = onlineCount.intValue();new Integer(count-1 );"OnlineCount" ,onlineCount);
web.xml配置
<listener > <listener-class > com.sise.listener.SessionListener</listener-class > </listener >
index.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
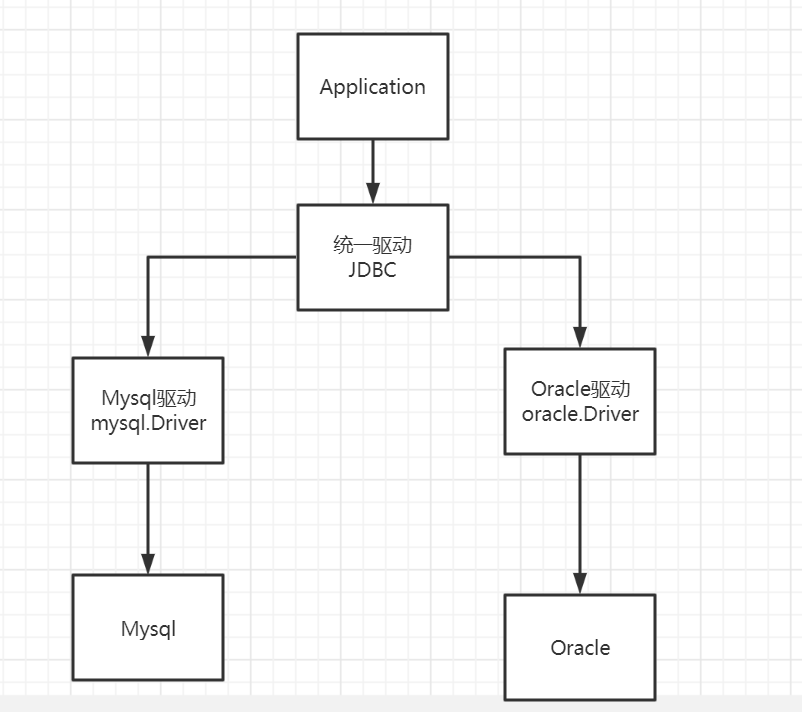
Filter权限拦截 JDBC jdbc:Java连接数据亏
maven依赖:mysql连接驱动
JDBC固定步骤:
加载驱动
连接数据库
向数据库发送SQL对象statement
编写SQL
执行SQL
关闭连接
导入maven依赖
<dependency > <groupId > mysql</groupId > <artifactId > mysql-connector-java</artifactId > <version > 5.1.47</version > </dependency >
新建数据库
编写Java代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class JdbcTest public static void main (String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=true" ;"root" ;"123456" ;"com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" );"select * from users" ;while (resultSet.next()){"id" ));"name" ));"sno" ));
预编译:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class JdbcTest1 public static void main (String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=true" ;"root" ;"123456" ;"com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" );"insert into users(id,name,sno) values (?,?,?)" ;1 ,4 );2 ,"小刘" );3 ,"454545" );int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();if (i>0 ){"插入成功" );
事务:
要么成功要么失败
ACID原则:保证数据的安全
开启事务